Python Dictionary For Loop Generate Keys
Posted : admin On 16.04.2020Mar 01, 2018 Python How to iterate Dictionary Key and Value pairs loop. 08 Beginner's Guide to Python - Dictionaries and For Loops - Duration: 10:32. London App Developer 14,222 views. Note that the restriction with keys in Python dictionary is only immutable data types. Python Split dictionary of lists to list of dictionaries. Generate link.
- Python Dictionary For Loop Generate Keys In Word
- Dictionary Python For Loop
- Python Dictionary For Loop Generate Keys Pdf
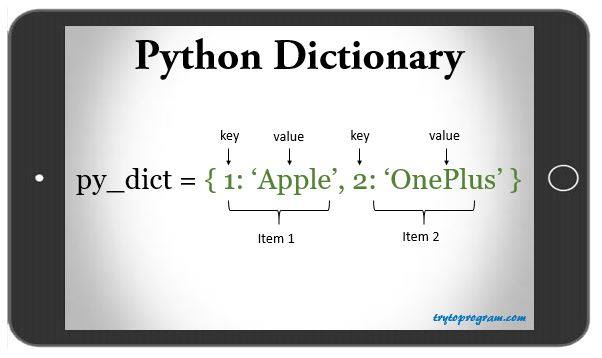
Dictionary
A dictionary is a collection which is unordered, changeable and indexed. In Python dictionaries are written with curly brackets, and they have keys and values.
Example
Create and print a dictionary:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
print(thisdict)
Accessing Items
You can access the items of a dictionary by referring to its key name, inside square brackets:
Example
Get the value of the 'model' key:
Try it Yourself »There is also a method called get() that will give you the same result:
Example
Get the value of the 'model' key:
Try it Yourself »Change Values
You can change the value of a specific item by referring to its key name:
Example
Change the 'year' to 2018:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict['year'] = 2018
Loop Through a Dictionary
You can loop through a dictionary by using a for loop.
When looping through a dictionary, the return value are the keys of the dictionary, but there are methods to return the values as well.
Example
Print all key names in the dictionary, one by one:
Try it Yourself »Example
Print all values in the dictionary, one by one:
Try it Yourself »Example
You can also use the values() function to return values of a dictionary:
Example
Loop through both keys and values, by using the items() function:
Login to remote host and edit /etc/ssh/sshdconfig file then restart ssh service. There are many ways to do so, here is one example.Or you can simply copy paste your public key content to remote host root user's authorizedkeys file.2nd step:Configure ssh to permit passwordless login in remote host. Generate ssh key ubuntu putty. In order to login to remote host as root user using passwordless SSH follow below steps.1st Step:First you have to share local user's public key with remote host root user's authorizedkeys file.
Try it Yourself »Check if Key Exists
To determine if a specified key is present in a dictionary use the in keyword:
Example
Check if 'model' is present in the dictionary:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
if 'model' in thisdict:
print('Yes, 'model' is one of the keys in the thisdict dictionary')
Dictionary Length
To determine how many items (key-value pairs) a dictionary has, use the len() method.
Example
Print the number of items in the dictionary:
Try it Yourself »Adding Items
Adding an item to the dictionary is done by using a new index key and assigning a value to it:
Example
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict['color'] = 'red'
print(thisdict)
Removing Items
There are several methods to remove items from a dictionary:
Example
The pop() method removes the item with the specified key name:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict.pop('model')
print(thisdict)
Example
The popitem() method removes the last inserted item (in versions before 3.7, a random item is removed instead):
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict.popitem()
print(thisdict)
Example
The del keyword removes the item with the specified key name:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
del thisdict['model']
print(thisdict)
Example
The del keyword can also delete the dictionary completely:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
del thisdict
print(thisdict) #this will cause an error because 'thisdict' no longer exists.
Example
The clear() method empties the dictionary:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict.clear()
print(thisdict)
Copy a Dictionary
You cannot copy a dictionary simply by typing dict2 = dict1, because: dict2 will only be a reference to dict1, and changes made in dict1 will automatically also be made in dict2.
There are ways to make a copy, one way is to use the built-in Dictionary method copy().
Example
Make a copy of a dictionary with the copy() method:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
mydict = thisdict.copy()
print(mydict)
Another way to make a copy is to use the built-in method dict().
Example
Python Dictionary For Loop Generate Keys In Word
Make a copy of a dictionary with the dict() method:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
mydict = dict(thisdict)
print(mydict)
Nested Dictionaries
A dictionary can also contain many dictionaries, this is called nested dictionaries.
Example
Dictionary Python For Loop
Create a dictionary that contain three dictionaries:
'child1' : {
'name' : 'Emil',
'year' : 2004
},
'child2' : {
'name' : 'Tobias',
'year' : 2007
},
'child3' : {
'name' : 'Linus',
'year' : 2011
}
}
Python Dictionary For Loop Generate Keys Pdf
Or, if you want to nest three dictionaries that already exists as dictionaries:
Example
Create three dictionaries, than create one dictionary that will contain the other three dictionaries:
'name' : 'Emil',
'year' : 2004
}
child2 = {
'name' : 'Tobias',
'year' : 2007
}
child3 = {
'name' : 'Linus',
'year' : 2011
}
myfamily = {
'child1' : child1,
'child2' : child2,
'child3' : child3
}
The dict() Constructor
It is also possible to use the dict() constructor to make a new dictionary:
Example
# note that keywords are not string literals
# note the use of equals rather than colon for the assignment
print(thisdict)
Dictionary Methods
Python has a set of built-in methods that you can use on dictionaries.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all the elements from the dictionary |
| copy() | Returns a copy of the dictionary |
| fromkeys() | Returns a dictionary with the specified keys and value |
| get() | Returns the value of the specified key |
| items() | Returns a list containing a tuple for each key value pair |
| keys() | Returns a list containing the dictionary's keys |
| pop() | Removes the element with the specified key |
| popitem() | Removes the last inserted key-value pair |
| setdefault() | Returns the value of the specified key. If the key does not exist: insert the key, with the specified value |
| update() | Updates the dictionary with the specified key-value pairs |
| values() | Returns a list of all the values in the dictionary |